If your website isn’t showing up in Google search results, it might not be indexed yet. Indexing is one of the most critical steps in getting your website noticed online. Without it, your content won’t appear in search engine results, no matter how well it’s written or how relevant it is.
In this guide, you’ll learn how Google indexing works, how to make sure your site is being crawled and indexed correctly, and how to fix common indexing issues. Whether you’re managing a blog, an eCommerce store, or a service-based site, this article will help you improve your online visibility step-by-step.
What is Google Indexing?
Google indexing is the process by which Google’s search engine discovers and adds web pages to its index. This index is essentially a massive database of all the web pages Google knows about.
When your site is indexed, it becomes eligible to appear in search results. The index is updated regularly, allowing new and updated pages to be found by users searching on Google.
So, when we talk about being “indexed by Google,” we’re referring to having your web pages stored in Google’s searchable library of content.
Kickstart Your Online Growth Right Away!
Start with essential SEO strategies to boost your website’s visibility and start attracting organic traffic.
Understanding Google Search: How Google Indexing Works
Before diving into indexing, it’s essential to understand how Google Search works. This knowledge lays the foundation for effective SEO and ensures your content is discoverable by your target audience.
Google Search operates through three primary processes: crawling, processing & indexing, and ranking.
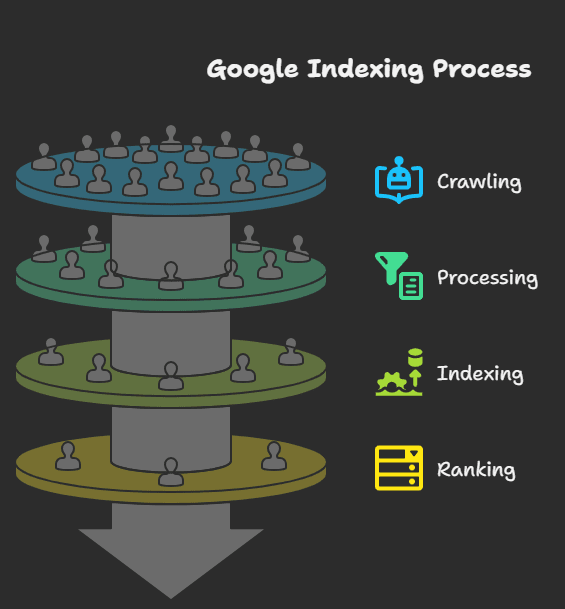
Crawling
Google uses automated software called web crawlers or “Googlebots” to browse the web. These bots follow links from one page to another, constantly discovering new or updated content.
They scan web pages, download them, and add them to a queue for indexing. Crawling doesn’t guarantee indexing, but it’s the first critical step. If your site can’t be crawled, it can’t be indexed or ranked.
Processing and Indexing
After a page is crawled, Google analyzes its content, structure, meta tags, and other elements to understand what it’s about. This includes evaluating text, images, video, internal links, and more.
Google then stores this information in its search index, a vast database containing hundreds of billions of web pages. Pages in the index are eligible to appear in Google search results.
Ranking
Once your pages are indexed, Google uses complex algorithms to rank them based on relevance, content quality, authority, user intent, and many other factors.
Pages that best match a user’s query and offer a good user experience are ranked higher in search results. This is why optimizing your content, both technically and contextually, is essential for visibility.
Google’s search system is designed to provide fast, accurate, and useful answers to users. By understanding these three core processes (crawling, indexing, and ranking), you can create a website that’s both user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
Does Google AI Mode Affect the Indexing Process?
As Google evolves, its use of artificial intelligence (AI) in search continues to grow. One common question among website owners and SEO professionals is: Does Google’s AI mode impact how websites are crawled and indexed?
Let’s explore how AI fits into Google’s indexing process and what it means for your website.
Understanding Google’s AI in Search
Google’s AI technologies, such as RankBrain and BERT, help the search engine better understand user intent and the context of queries. These tools don’t directly affect crawling or indexing, but they enhance how indexed content is interpreted and ranked.
In short, AI influences what content is shown in response to a query, not necessarily whether that content is indexed in the first place.
Comprehensive Comparative Analysis: LLMO vs SEO
Indexing Still Relies on Core Technical Signals
Despite AI advancements, the fundamentals of indexing remain the same. Google still relies on:
- Crawling your site
- Analyzing technical elements (meta tags, structured data, robots.txt)
- Evaluating content accessibility and quality
Even in “AI mode,” if a page is blocked from crawling, contains a noindex tag, or lacks quality signals, it may not be indexed at all.
AI Enhances Content Understanding, Not Discovery
While AI helps Google understand meaning, nuance, and relationships within your content, it does not replace the indexing system.
For example, BERT helps process natural language queries better, but it works after your page is indexed. So, optimizing for AI means creating content that is clear, useful, and well-structured, rather than trying to game the system.
Future of SEO: Integrating AIO, GEO, AEO, and SXO Strategies
So far, we’ve seen that Google’s AI tools don’t directly affect whether a page is indexed, but they do play a role in how content is ranked and displayed once it is indexed.
Before we move into setting up Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools), it’s important to remember: indexing success still depends on technical SEO, site structure, and content quality, not just AI optimization.
Let the Experts Handle Your Site’s SEO
From content to backlinks, we manage your entire SEO process, so you can focus on your business.
Setting Up Google Search Console
To take control of how your website appears in Google Search, you need the right tools and Google Search Console (GSC) is one of the most powerful and essential ones available.
It’s a free tool provided by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site’s visibility in search results.
Whether you’re launching a new website or managing an established one, setting up Search Console should be one of your first SEO steps.
Why Google Search Console Matters?
GSC doesn’t just help you monitor indexing; it gives you direct insight into how Google views your site. It shows:
- Whether your pages are being crawled and indexed
- If there are any issues blocking visibility
- Which keywords are driving organic traffic
- How users interact with your search listings
In short, it bridges the gap between your content and Google’s search algorithms.
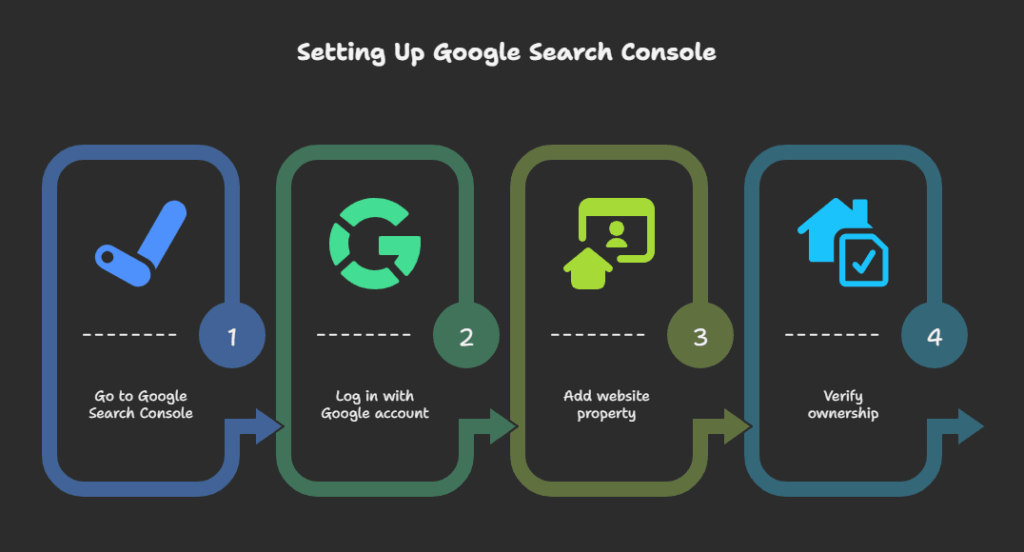
Step-by-Step: How to Set It Up
Setting up your GSC account is simple. Head over to Google Search Console and use the Google account associated with your website or business to login. Next, add your website property.
There are two types of properties:
- Domain Property: Covers all subdomains and protocols (e.g., http, https, www)
- URL Prefix: More limited, tracks only the specific URL path you enter
It’s best to select the domain property for full tracking coverage.
Verify Your Website
Google needs to confirm you’re the rightful owner. You can verify using:
- DNS Record: Preferred method for domain properties
- HTML Tag: Add a meta tag to your homepage
- Google Analytics: Use your existing GA tracking
- Google Tag Manager: If installed on your site
Once verified, Google will begin collecting data for your site.
Key Tools Available After Setup
Once your property is verified, Google Search Console opens up a suite of tools and reports to help you improve indexing and performance:
URL Inspection Tool: This tool lets you check how a specific page is indexed. You can:
- See if it’s in Google’s index
- Test live URL status
- Request indexing for new or updated pages
- Review structured data and AMP details
Coverage Report: The coverage report shows which pages:
- Are indexed successfully
- Have indexing errors
- Are excluded (with reasons like “noindex tag” or “duplicate”)
This is essential for identifying and fixing indexing issues.
Sitemaps: Submit your XML sitemap (e.g., https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml) to help Google discover your pages more efficiently. This ensures new or updated content gets crawled faster.
Performance Report: Get detailed insights into how your site performs in Google Search:
- Total clicks and impressions
- Average click-through rate (CTR)
- Average position in search results
- Search queries driving traffic
You can filter the data by page, query, country, device, and more to refine your SEO strategy.
What Happens Next?
After setup, give GSC some time to start collecting data. Within a few days, you’ll begin to see:
- Which pages has Google indexed
- Any technical issues affecting indexing
- What keywords are your pages ranking for
From here, you can start optimizing your content, fixing issues, and submitting new URLs for indexing.
Fix What’s Holding Your Rankings Back
Optimize site speed, crawlability, and indexing issues with expert technical SEO solutions.
Common Issues with Indexing
Sometimes, even good content doesn’t get indexed. Here are some common issues that might block your pages:
- Noindex Tag: This meta tag tells Google not to index a page. Remove it from any page you want to appear in search results.
- Duplicate Content: Pages that are too similar to each other can be seen as duplicates. Use canonical tags to tell Google which version to prioritize.
- Nofollow Links: Internal links with rel=”nofollow” can prevent link juice from flowing, making it harder for Google to discover and prioritize those pages.
- Crawl Budget Limits: For larger websites, Google only crawls a certain number of pages in a given period. Optimize site speed and internal linking to make the most of your crawl budget.
- Blocked in Robots.txt: Your robots.txt file might unintentionally be blocking important pages from being crawled.
Optimizing Your Website for Google Indexing
To increase the chances of your site getting indexed quickly and correctly, follow these best practices:
- Create Quality Content: Google prioritizes pages that are helpful, informative, and unique. Write for your audience, not just for algorithms.
- Use Descriptive URLs: Avoid numbers or symbols in URLs. Use keywords that describe the page, like
/how-to-index-a-website.
- Optimize Images: Use alt text and compress images to help with both indexing and page speed.
- Maintain a Clear Site Structure: Group related content together. Use categories, tags, and breadcrumb navigation where applicable.
- Internal Linking: Ensure every important page has multiple internal links pointing to it. This helps Google discover “orphan pages” (pages not linked to from anywhere else on your site).
- Use Canonical Tags: These tags prevent duplicate content issues by telling Google the “preferred” version of a page.
- Optimize Meta Tags: Write compelling and keyword-rich meta titles and descriptions. Though not direct ranking factors, they affect CTR and indexing.
Submitting URLs to Google to Index
There are two primary ways to request indexing:
- URL Inspection Tool: Paste a URL into the tool in Google Search Console and click “Request Indexing.” This is ideal for new or updated pages.
- XML Sitemap: Submit your full sitemap (e.g., https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml) in the GSC Sitemaps section. This helps Google discover and index multiple pages efficiently.
Indexing requests can take a few days to a few weeks, depending on crawl frequency and other technical factors.
Internal and External Linking
Internal links help Google navigate your site. Link related blog posts, service pages, and resources together. Avoid using nofollow attributes for internal links, unless necessary. Make sure:
- Important pages have more internal links
- Every page is reachable in a few clicks from the homepage
- You don’t have orphan pages
External Links refers to linking to authoritative sources improves trust and credibility. It can also indirectly help indexing, especially if authoritative sites link back to you.
Encourage external websites to link to your best content. This helps with both indexing and rankings.
Learn more: How to Fix Broken Links After WordPress Migration
Measuring Indexing Success
You can’t improve what you don’t track. Here’s how to measure how well your site is being indexed. The tools to use are:
- Google Search Console: Check coverage, errors, and index status
- Google Analytics: Track organic traffic to indexed pages
- Third-party SEO Tools: Use tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Screaming Frog to crawl your site and find indexing issues
Key Metrics to monitor are:
- Number of pages indexed
- Pages excluded (and why)
- Impressions and clicks from organic search
- Crawl stats and errors
Over time, regularly checking these metrics will help you identify and fix issues before they hurt your traffic or rankings.
Check out: Best Website Audit Tools for SEO
Conclusion
Getting your website indexed by Google is the first step toward building a strong online presence. Without indexing, your content won’t show up in search results, no matter how good it is.
By setting up Google Search Console, optimizing your site structure, fixing indexing issues, and actively submitting URLs, you ensure that Google can discover and understand your content.
Internal links, high-quality content, and technical SEO improvements all work together to boost your indexing and, ultimately, your rankings.
Stay proactive. Keep monitoring your index status, update your content regularly, and always aim to provide value to your visitors.
By following this guide, you’ll not only get your website indexed but also position it for long-term success in Google Search.
FAQs About Google Indexing
How do I get Google to index my website?
To get Google to index your website, make sure your site is crawlable and optimized for search. Create high-quality content, use internal links to connect relevant pages, and ensure that Google crawling is not blocked by your robots.txt file or noindex tags. Submitting a sitemap URL in Google Search Console also helps Google find and index all the pages on your site, including new pages and individual URLs.
How do I submit my website to Google for indexing?
You can submit your website to Google by uploading your XML sitemap to Google Search Console. Additionally, you can paste individual page URLs into the URL Inspection Tool and click “Request Indexing.” This tells search engines that your content is ready to be crawled. Internally linking your pages also helps Google discover them faster.
How do I make my website searchable on Google?
To make your website searchable on Google, ensure it’s accessible, mobile-friendly, and technically optimized. Use descriptive URLs and proper meta tags, and avoid nofollow internal links that prevent page discovery. Internally link to important pages and keep your content updated so Google can find and rank it. Also, check that your HTTP headers and robots settings don’t unintentionally block Google.
Why won’t Google index my website?
Google might not index your website for several reasons: noindex tags, blocked crawling via robots.txt, poor-quality or duplicate content, or a lack of internal links pointing to new pages. Make sure that pages on your site are accessible and not orphaned. If indexing issues persist, use the Coverage Report in Google Search Console to identify and resolve errors. Also, make sure your sitemap is correctly submitted and includes relevant pages from your entire site.